The two algorithm changes Google Penguin Update of April 2012 and the Google Penguin Update 2.0 had the target of identifying webspam in the search results and, in turn, inflicted a penalty for violations of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
- How do I know that a website is affected by the Google Penguin update?
- What does an unnatural link profile look like?
- SISTRIX Training: Google Penguin Update - analysing the link profile
- Natural or unnatural link profile?
- How to check a website for inferior backlinks?
- Use LinkRating for an automated link audit and risk evaluation
The Google Penguin algorithm looked for unnatural link profiles of websites. If a link profile of a website was identified as unnatural by the algorithm, the domain received a penalty,
How do I know that a website is affected by the Google Penguin update?
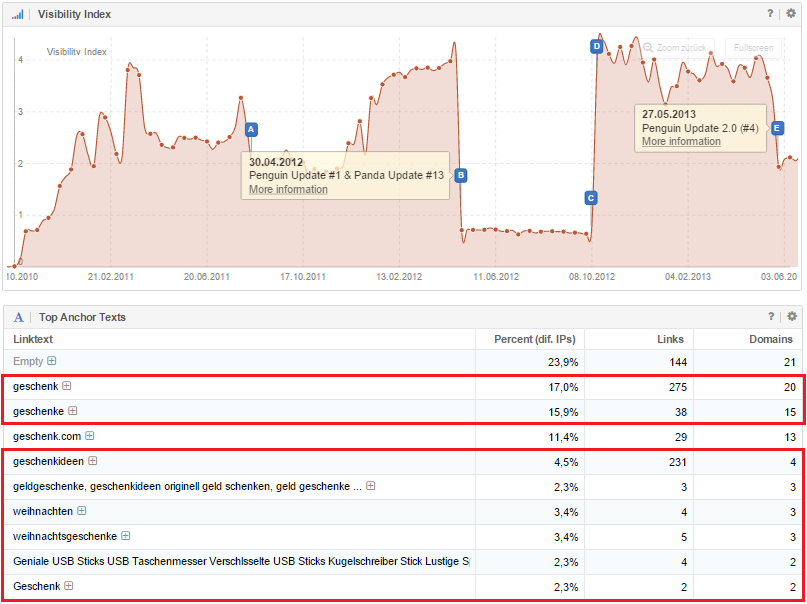
When you are analysing a domain in the SISTRIX Toolbox, you can gain valuable insights into the most important Google-updates by using the Visibility history for the domain, together with the event pins. These will give you a first impression of whether a website is, or was, affected by the Google Penguin update.
If you notice a massive decline of the Visibility Index value of a domain from one calendar week to the next and an event pin “Penguin Update” is shown for the week, you have a very good indicator that the page may well have been hit by a webspam algorithm penalty.
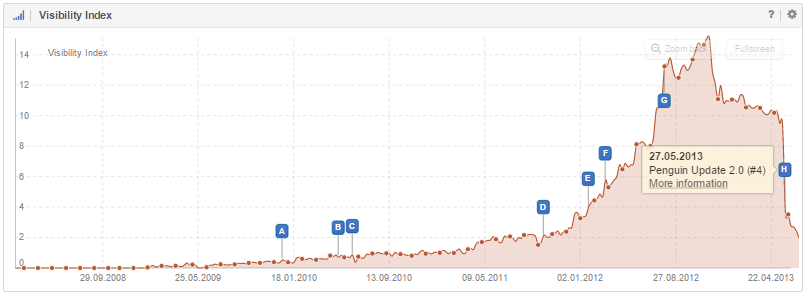
A website can be affected by the Penguin Update and its iterations multiple times:
In both examples, the Penguin Update, marked with an event pin, is a possible cause for the drastic loss of visibility. Here, it is important to check the affected websites to see if the have an unnatural link profile.
What does an unnatural link profile look like?
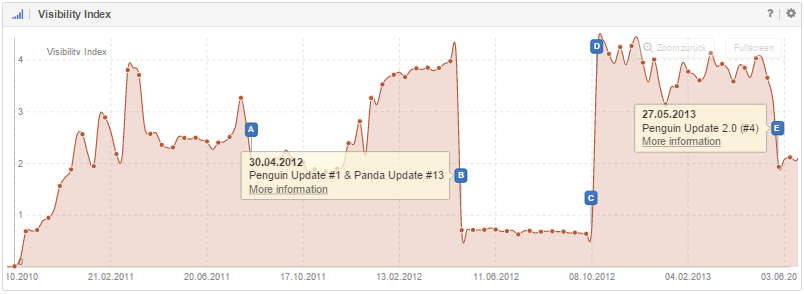
An unnatural link profile exhibits a proportionally high amount of hard linktexts compared to links which were created naturally.
For the two examples above, their linktexts looked as follows:
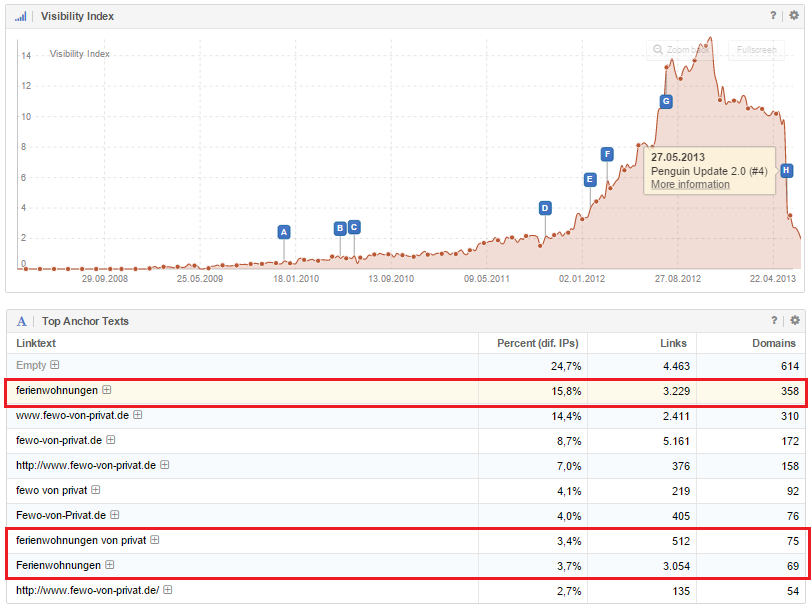
Even if a website has recovered from the Penguin filter, it can be caught in it, once again, as is shown by the following example:
SISTRIX Training: Google Penguin Update – analysing the link profile
Natural or unnatural link profile?
You would like to get a rough estimate of whether your own link profile appears natural without having to look at the quality of the backlinks in detail? This can be done quite easily:
- Tutorial: Tips for detecting a natural link profile.
How to check a website for inferior backlinks?
The SISTRIX Toolbox link module offers comprehensive ways to dissect a website for inferior links:
Use LinkRating for an automated link audit and risk evaluation
Would you like the SISTRIX Toolbox to automatically rate the quality of your backlink profile and tell you exactly why we think so?