Duplicate content refers to duplicated content that can be reached via multiple URLs. This so-called duplicate content should be avoided at all costs. Each piece of content on a website must only ever be accessible through one unique URL. Otherwise, Google is presented with the problem of determining which URL should be displayed in the rankings and which positive ranking signals should be assigned to which URL.
- What is Duplicate Content?
- Difference: Internal and External Duplicate Content
- Example of Internal Duplicate Content
- Example of External Duplicate Content
- What Duplicate Content is Not
- Is Duplicate Content a Problem?
- Google Attempts to Solve Duplicate Content Problems on Its Own
- Checking Your Website for Duplicate Content
- Our Google Conclusion
- Video: Google Q&A on Duplicate Content
- Additional Information on This Subject
- SISTRIX
Discover how SISTRIX can be used to improve your search marketing. 14 day free, no-commitment trial with all data and tools: Test SISTRIX for free
What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content, often abbreviated to “DC”, is the presence of identical content on one or more websites. A distinction is made between internal duplicate content and external duplicate content.
Internal duplicate content can result simply by having identical content on the same website available under multiple URLs – for example, through the parameters of a filter that are included in the URL.
External duplicate content can occur when a website is available in multiple language versions, but appears with more than one language version in the search results on the same search market (e.g., google.co.uk).
Difference: Internal and External Duplicate Content
Internal duplicate content is limited to your own domain / hostname.
External duplicate content is domain-overlapping, i.e., it occurs on two or more domains.
Example of Internal Duplicate Content
Online shops, for example, frequently have to deal with internal duplicate content. Often, product detail pages are also directly accessible without the corresponding category and/or product page:
- http://www.onlineshop-domain.com/category/productpage/productdetailpage
- http://www.onlineshop-domain.com/productdetailpage
These contents are then readily indexed by search engines if both URLs are linked to externally. Another reason can be inconsistent internal linking.
Example of External Duplicate Content
Many websites can be accessed via multiple domain names. There is nothing wrong with this, as long as all other domain versions redirect to the corresponding main domain using a 301 redirect.
If this is not the case, Google is confronted with different domains that all offer the same content. This makes it difficult for the Google-Bot to determine the relevance of each individual page, which can lead to ranking problems for the website.
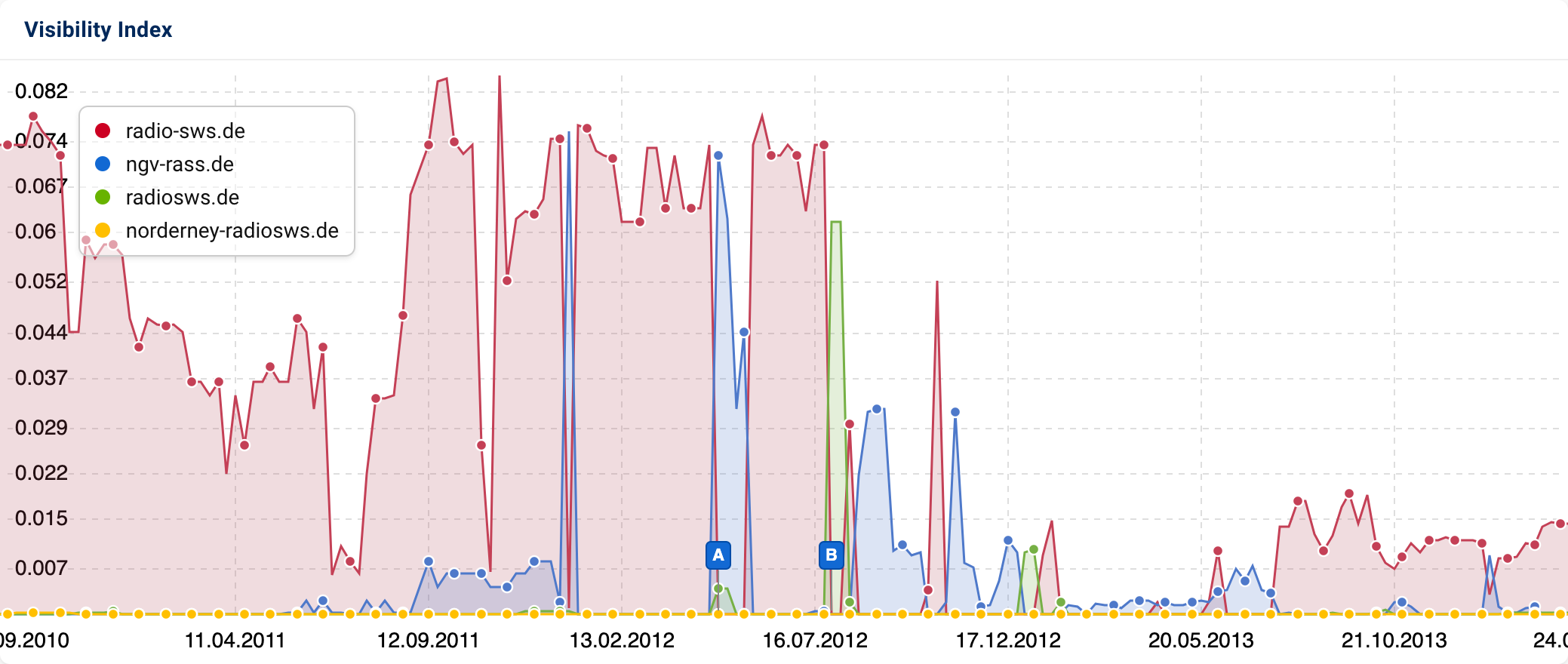
Evidently, the domain radio-sws.de is the desired main domain. The content of the website radio-sws.de can be found in identical form on three other domains. That is how duplicate content is created due to multiple domain names for one website. Google is not always sure which of the four domains is relevant to the topic, and therefore alternately ranks one page and then the other.
What Duplicate Content is Not
If a piece of content is available in multiple language versions, this is not considered duplicate content. Citations or cited paragraphs are also not identified as duplicate content.
However, when citing content, it is important to ensure that the semantic mark-up in the source code is correct:
<blockquote>Here is the quoted text - <cite>Here is the name of the quoted author or source</cite></blockquote>Is Duplicate Content a Problem?
Yes! Duplicate content is not unique and does not offer the users any added value. From Google’s point of view, duplicate content may even be compared to attempted fraud in a few cases when texts are copied from other websites without a licence.
DC impedes Google in its quest to find the best possible result for the user. This is why duplicate content should be taken seriously by webmasters.
Duplicate content can be responsible for fluctuations in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages), i.e., the rankings of a website, as it is unclear to Google which page offers the most relevant content for a requested search query. Thus, the target URLs in the search results can freely switch around.
Google Attempts to Solve Duplicate Content Problems on Its Own
Google tries to identify duplicate content on its own and decides independently which content is the most relevant to the user’s search request – and displays this result in the SERPs.
During the preceding content indexation, Google also tries to identify the best possible version (URL) of the duplicated contents and indexes only that – if possible.
If the rankings and traffic of a website are consistent despite an existing DC problem and fluctuating numbers of indexed pages, the duplicate content problem is not a threat to the website’s performance, for the time being.
Checking Your Website for Duplicate Content
The SISTRIX Onpage projects offer an automated onpage analysis of your websites and show you all SEO-relevant errors and notices. Each type of error comes complete with its own explanation and concrete guidelines for improvements, which help to introduce you to the Onpage optimisation for your website.
Duplicate content is displayed in detail for each individual URL.
In the free trial phase of SISTRIX, you have access to all modules – including the Onpage analysis projects wherein you can examine your website for duplicate content, among other things. Try SISTRIX for free in the two-week trial period – without any hidden costs or subscriptions.
What Google says
Google tries hard to index and show pages with distinct information. (...) However, in some cases, content is deliberately duplicated across domains in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings or win more traffic. Deceptive practices like this can result in a poor user experience, when a visitor sees substantially the same content repeated within a set of search results.
Source: Google Search Console Help
Our Google Conclusion
From Google’s point of view, duplicate content does not provide users with any added value and can even be classified as spam if text is simply copied from other pages. The duplicates prevent Google from finding the best possible result for the user. External duplicate content does not always and certainly not immediately lead to a Google penalty, but a persistent DC problem can cause lasting damage to the website.
Video: Google Q&A on Duplicate Content
Additional Information on This Subject
- Avoid duplicate content – Google Search Console Help
SISTRIX
- Google on Duplicate-Content – SISTRIX Blog
- De-duplication of Search Results: A Complex Example – SISTRIX Blog
Test SISTRIX for Free
- Free 14-day test account
- Non-binding. No termination necessary
- Personalised on-boarding with experts